Studies have long demonstrated that strong local journalism can encourage higher voter turnout, counter polarizing narratives, expose corruption, and lead to people feeling a strong sense of community.
We’ve seen much of this show up anecdotally in the local news ecosystems that Democracy Fund supports. We define a news ecosystem as the network of institutions, collaborations, and people that local communities rely on for news, information, and engagement. This approach puts people and places squarely at the center of our goals and vision.
When we launched our new Equitable Journalism strategy in 2023, we wanted to learn even more about how journalism is strengthening democracy. We recently partnered with Impact Architects (IA) to revisit the Healthy News & Information Ecosystem framework. This framework was initially built in 2020 in partnership with Impact Architects, Knight Foundation, and Google News Initiative to share models for understanding the health and evolution of local news ecosystems with other funders who were considering funding local news. The graphic below illustrates the four layers of data that our updated model uses to understand local news ecosystems:
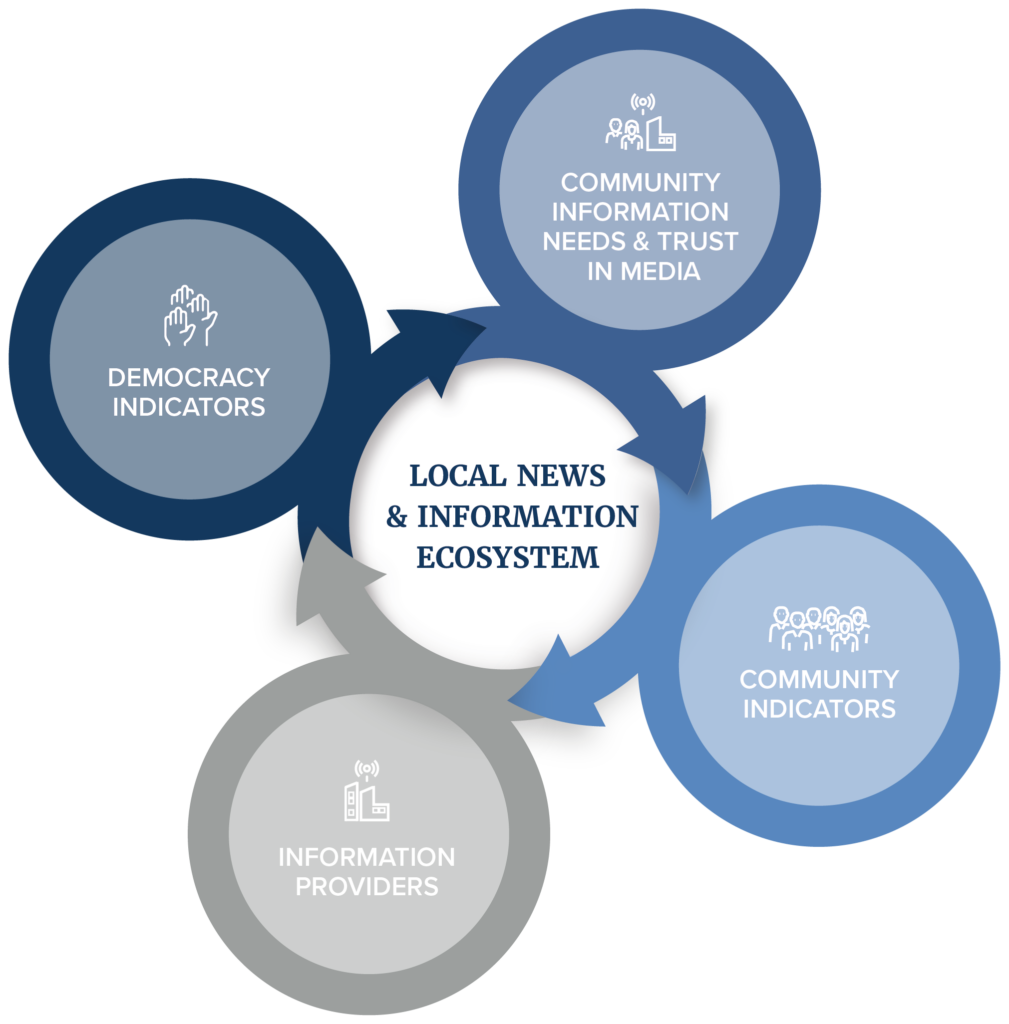
This new “Democracy Indicators” layer provides a deeper understanding of how Democracy Fund’s vision of an inclusive multiracial democracy is coming to life, community by community. Some examples of data we’re taking into consideration include:
- the availability of legal resources for local journalists;
- the relative difficulty of voting for residents in different states;
- and the percentage of residents who have recently contacted a public official, attended a political demonstration, and/or donated to a political candidate or organization.
Through these indicators we want to understand how expanding access to local news and information can result in deeper engagement with our democracy. We can then pair this layer of research with even deeper dives in ecosystems that include more community listening and collaboration.
How Democracy Fund Thinks About Local News Ecosystems
At Democracy Fund, we’ve invested over $15.75 million in local news ecosystems across the US since 2016. If our work is successful, then communities will have access to news and information that advances justice, confronts racism and inequality, and equips people to make change and thrive, wherever they live.
Over the years, we’ve seen exciting signs of progress:
- In New Jersey, the state has allocated millions of dollars to bolster community media, building on years of community-informed organizing.
- In North Carolina, media makers from the western mountains to the eastern coast are receiving recognition and resources for their work.
- In New Mexico, more people have more opportunities to get involved in news gathering and reporting, including a fellowship program to help recent grads stay in-state.
- The local news ecosystem funding model is also growing. Press Forward, a national coalition investing more than $500 million to strengthen local journalism, launched the Press Forward Local network modeled on this news ecosystem approach, which quickly grew to 25 chapters of local funder coalitions in its first year.
Findings from the Latest Research
While we purposefully didn’t rank the ten ecosystems that Democracy Fund explored overall because of their variety and diversity, the latest research shows there are still many promising themes that can be found across them, especially when we consider the ecosystems in different stages of their development.
Strong ecosystems (Chicago, Michigan, and New Jersey)
Strong ecosystems generally have higher than average indicators across most if not all of the four categories in the graphic above. There is evidence of a relationship among information providers, community, and civic engagement and democracy. These strong ecosystems demonstrate more consistency across the entire ecosystem. For example, this could be more equal access to information across various racial, ethnic, and/or linguistic groups.
Emergent ecosystems (Colorado, Georgia, New Mexico, and North Carolina)
Emergent ecosystems generally score higher than average across many of the indicators and/or groups of indicators and show evidence of gathering momentum. However, they still have gaps in information providers and/or access for significant segments of the population. Impact Architects also found less evidence of connection among information providers, community, and civic engagement in these ecosystems.
Ecosystems ripe with opportunity (Arizona, Oklahoma, and Washington, D.C.)
These ecosystems score lower than average across many indicators or categories of indicators. They demonstrate significant need and opportunity with respect to information providers and support for community and civic engagement. In each ecosystem, there are examples of bright spots across an uneven landscape. For example, this could be one strong region within a larger ecosystem or one prominent organization that is helping local news thrive.
Under-resourced ecosystems
Under-resourced ecosystems score lower than average across some indicators and/or categories of indicators and demonstrate significant need across information providers. These ecosystems have information gaps in communities and uneven and/or low levels of civic engagement. Impact Architects did not identify any under-resourced ecosystems in this assessment. However, these local news ecosystems are large and complex and there are likely under-resourced areas within many of the identified ecosystems.
How We’re Using What We’ve Learned
We believe that this framework can support conversations, including our own at Democracy Fund, about how we can take a more nuanced approach to learning about communities’ news and information ecosystem health. We have invested in this space for nearly a decade, and there is a lot we can learn from the changes over time. One of the most powerful things equitable local news can do is build powerful relationships between people that help them make change in their lives — and that is hard to track. We hope to revisit this data in the coming years to understand more of the changes taking place.
There are many organizations and projects taking on this challenge that we are grateful to continue learning with on this journey. We hope this framework serves as a resource for the field and this cohort of organizations, and welcome further ideas, collaboration, and feedback on the themes and ideas within it.
This work would not have been possible without the many folks who contributed time to share thoughts and feedback on their ecosystems. Thank you for all you do in Arizona, Chicago, Colorado, Michigan, New Jersey, New Mexico, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Washington, D.C., and beyond.
Please reach out to learn more about Democracy Fund’s work with local news ecosystems.



