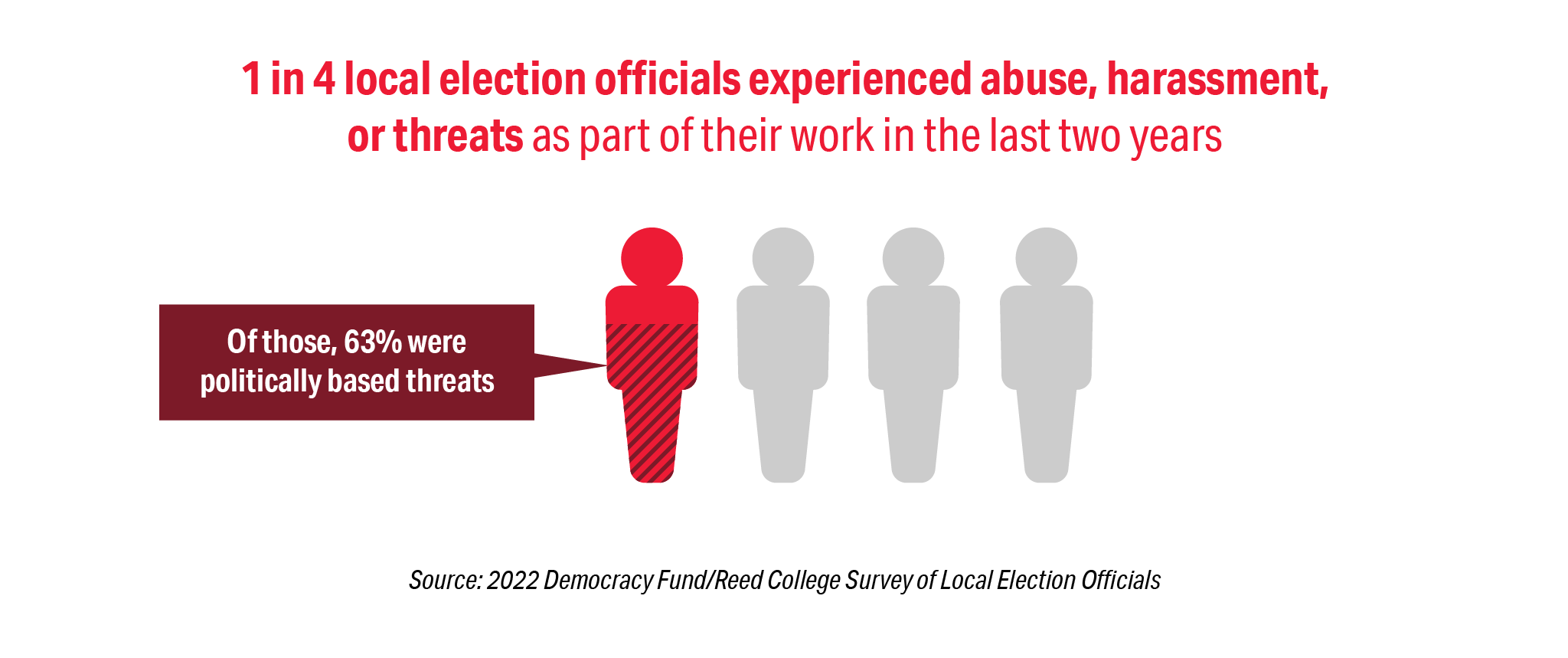
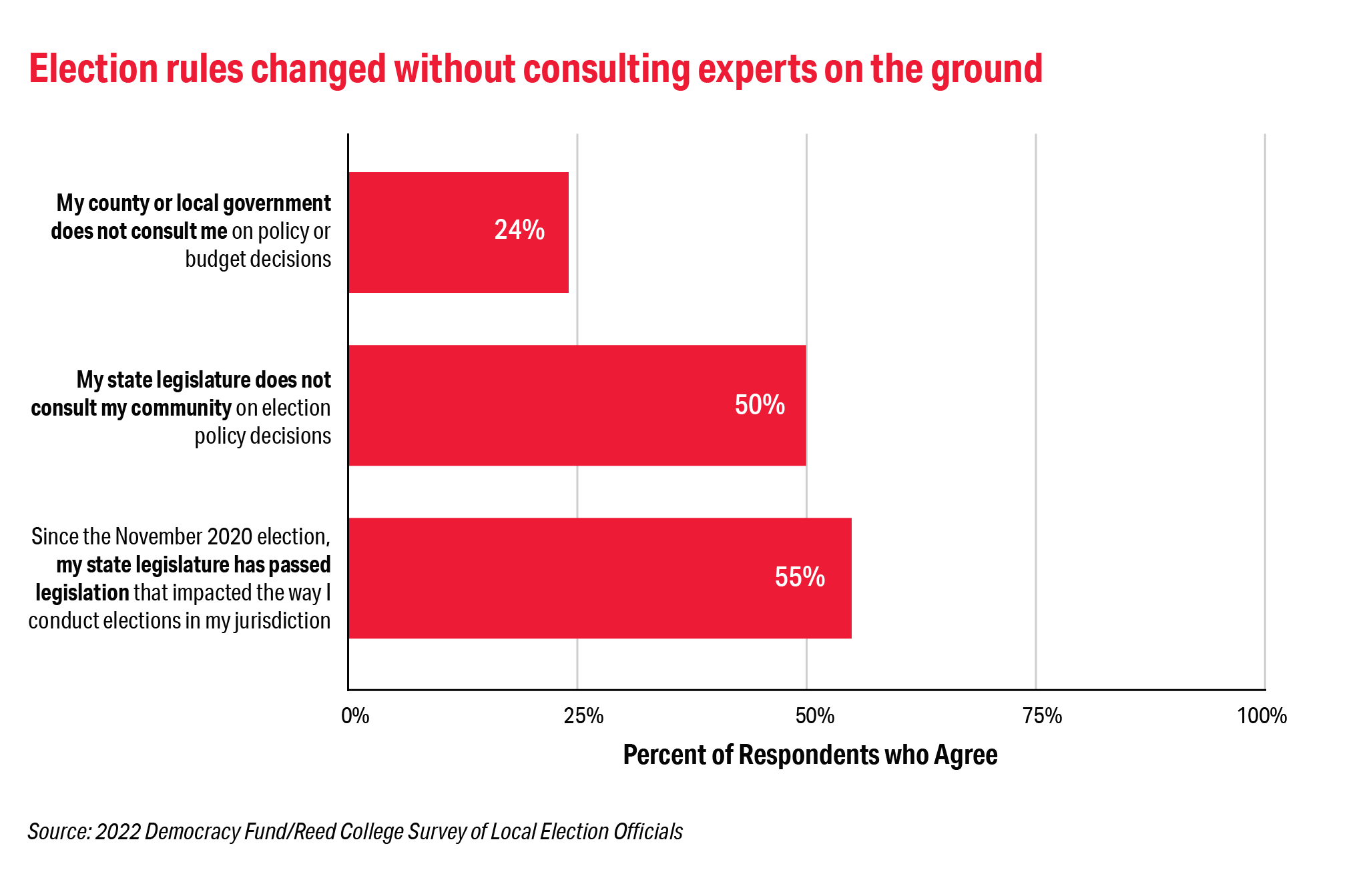
Climate change is here. Unfortunately, that means that many of us across the globe will soon need to leave our homelands. Within the United States, people are already leaving the rising waters of the Gulf Coast to seek refuge further north. Others are fleeing the wildfires and droughts of California for safer places. And at the southern border, migrants from all over the world (no longer just points further south) are seeking a safer life in the United States. Last year, 100 million people were displaced globally due to conflicts and crises — a new record. Climate change is multiplying this crisis. The UN estimates that over the next 30 years, about one billion of us will need to move.
What does this displacement mean for democracy in the United States? In a nutshell: as global migration reaches unprecedented levels, white supremacy is rising to meet it. This has dangerous consequences.
From the start, the founders of American democracy designed our governing system to exclude everyone but white, elite, male landowners. They built racism into our public institutions and society to exclude and marginalize people of color. As a way to protect this power structure, white nationalists have always pointed to migrants as a primary target for scapegoating. Today, white nationalists are using hostile, racist language to dehumanize migrants. This often leads to acts of discrimination and violence. It’s not surprising — this cycle has happened many times throughout this country’s history. But now that climate change is accelerating, we’re seeing it at a larger scale. It affects both migrants entering the United States from other countries, and migrants within the country.
Another factor to consider: our democracy is land-based. A person’s rights and representation are tied almost entirely to where they live. When we suddenly have to move, this becomes a problem. For example, an American citizen who flees a hurricane in South Carolina and takes refuge with family in Virginia still has a passport and basic protections under the Constitution. She could request an absentee ballot from her town in South Carolina, assuming the town is still functioning. But what happens when the impact of climate change is so extreme that an entire town or city is displaced? What would it mean for a city councilor, a state representative, or a member of Congress whose constituents all leave their districts?
At Democracy Fund, we are working to address these challenges. In April 2022, Democracy Fund announced our new organizational strategy with a commitment to investing in the power and leadership of communities of color to strengthen and expand the pro-democracy movement and undermine those who threaten the ideals of our inclusive, multiracial democracy. Over the past year, our Just and Inclusive Society program has revised its strategies in line with this new organizational strategy to better meet the moment we are in while building for the best version of our shared future.
Our new five-year strategy is the result of many thoughtful conversations with our grantees and experts from across the field. We cannot overstate how much we appreciate the experience, passion, and creativity of these organizations, whose staff are working on the frontlines of these issues. We look forward to continuing our collaborative approach with our grantees, as we aim for transformative impact together.
We are interested in hearing your thoughts on what elements excite you, and we know we have a weighty responsibility to help make these ideas a reality.
Building power for a welcoming and inclusive American democracy
We are working toward our vision of an American democracy that is welcoming and inclusive of all migrants and refugees, that actively supports their resettlement in a just and humane manner, and that builds social cohesion in the face of massive internal and external migration. To get there, we believe we need to support a broad-based intersectional social movement capable of inspiring hope over fear, instilling cooperation over competition, and instituting a sense of shared abundance over scarcity. At every step, the movement needs to be led by marginalized and most impacted communities who are integral members of the pro-democracy coalition fighting for a just and inclusive multi-racial democracy.
In support of this future, we will fund this intersectional movement through our Power-building in Marginalized Communities initiative. This initiative will focus on the intersectional movements led by refugees, migrants, and Black and brown communities. Our investments will support organizations and leaders to: (1) elevate stories and shift narratives around migration and refugeehood, (2) build a shared strategy and solidarity across movements, communities, and geographies, and (3) build power in marginalized communities.
This area of focus is a natural outgrowth of the work we began in 2017 to protect the civil rights and liberties of Black, African, Arab, Middle Eastern, Muslim, and South Asian (BAMEMSA) communities who were targeted by the Trump Administration. This earlier work provided legal and policy support to immigrant rights and racial justice work, and helped mitigate the risks of political violence resulting from a resurgent authoritarian faction.
Our new strategy has been informed by our conversations with our grantees and partners about how philanthropy needs to meet this moment in our democracy. We listened deeply to what grantees said is happening now, and what is on the horizon. Our new strategy takes those challenges head on, guided by an advisory group including the Rise Together Fund, El Hibri Foundation, the Pillars Fund, Ford Foundation, and Unbound Philanthropy.
Some changes you will see in our funding
In the next five years, we are reorienting our focus from BAMEMSA communities to include broader refugee and migrant communities that have been and will be displaced by climate change, as a subset of our wider interest in supporting all marginalized communities. Key to that work will be a shift from providing direct services, to building capacity, power, and momentum across communities that will be sending and receiving migrants.
A few of the key shifts include:
- Moving from prioritizing litigation to a power-building framework. We’re shifting from a responsive posture to one that proactively works to change the system. As the numbers of migrants increase, so too will the political rhetoric driven by fear, subverting or suppressing civil liberties and rights. We plan to focus on intervention points emerging from the increasing flow of migration and rising xenophobic and racist attacks by the authoritarian faction.
- Focusing on intersectional movement building led by migrant, refugee, and impacted communities. The growing number of organizations working in this arena are disconnected and insufficiently funded. To bolster the movement, we will begin investing in refugee organizing work, engage grassroots and national network organizations, and explore intermediaries that also have footprints at the regional, state, and local levels.
- Engaging place-based organizations. We will support organizations located in geographies that either are “sending” people to other places or “receiving” incoming migrants by funding the implementation of existing or experimental models of support for migrants and refugees (e.g., transitional justice mechanisms, mutual aid, community sponsorship, or resilience hubs).
As we begin implementing our new strategies, we’re motivated by the opportunities for learning and growth. We will be transparent, accessible, and accountable along the way. We are excited to invest in organizations that: demonstrate excellence in building and executing programs aligned with our strategic priorities; exhibit a solid racial justice analysis; employ BIPOC (Black, Indigenous and People of Color) in senior leadership roles; and work in concert with aligned efforts to build the power of marginalized communities.
Moving into the next five years
It’s clear that climate-induced mass migration and white nationalist authoritarianism are on a collision course, but efforts to protect vulnerable communities are also gaining momentum. The support we have seen in Washington, DC and New York City in response to migrants bussed there from Texas and Florida, is a powerful example. Community organizations are recruiting volunteers, enlisting local charities and churches, pressuring municipal governments, and controlling narratives. The community leaders in these cities are building a moral social movement that responds to need, supports the integration of migrant communities, and turns a tactic of division into an opportunity for solidarity and unity.
The challenges we face as a country and as a people over the coming decades are enormous. A key part of our new strategy will also be to partner with more and more funders to meet this moment.
There are still many decisions left about who and how we will fund to make this vision a reality. We’ll be sharing more information, updating our website, and considering new grantees in 2023 and we welcome your partnership and accountability along this journey. If you have questions about our new strategy, don’t hesitate to reach out. We are grateful for your partnership and energized for our collective future.